画图应用实战:画板
画图应用实战:菜单一文介绍了画图应用菜单的设计,本文介绍画板的内容。
1. 画板的逻辑
当用户按住屏幕,滑动鼠标或者手指时,画板会绘制出用户移动的轨迹。上述逻辑可以拆解为:画板监听用户的行为,当用户按住屏幕时,准备绘制线条;当用户移动时,每移动到一个新点,就绘制一条从上个点到新点的线;当用户停止时,绘制也停止。这里线条(Stroke)的起点是用户按下屏幕的地方,终点是用户释放的地方,它由一条条两点之间的线(Line)构成。系统需要记录所有用户绘制的线条(Stroke),画板每次会重新渲染这些线条。
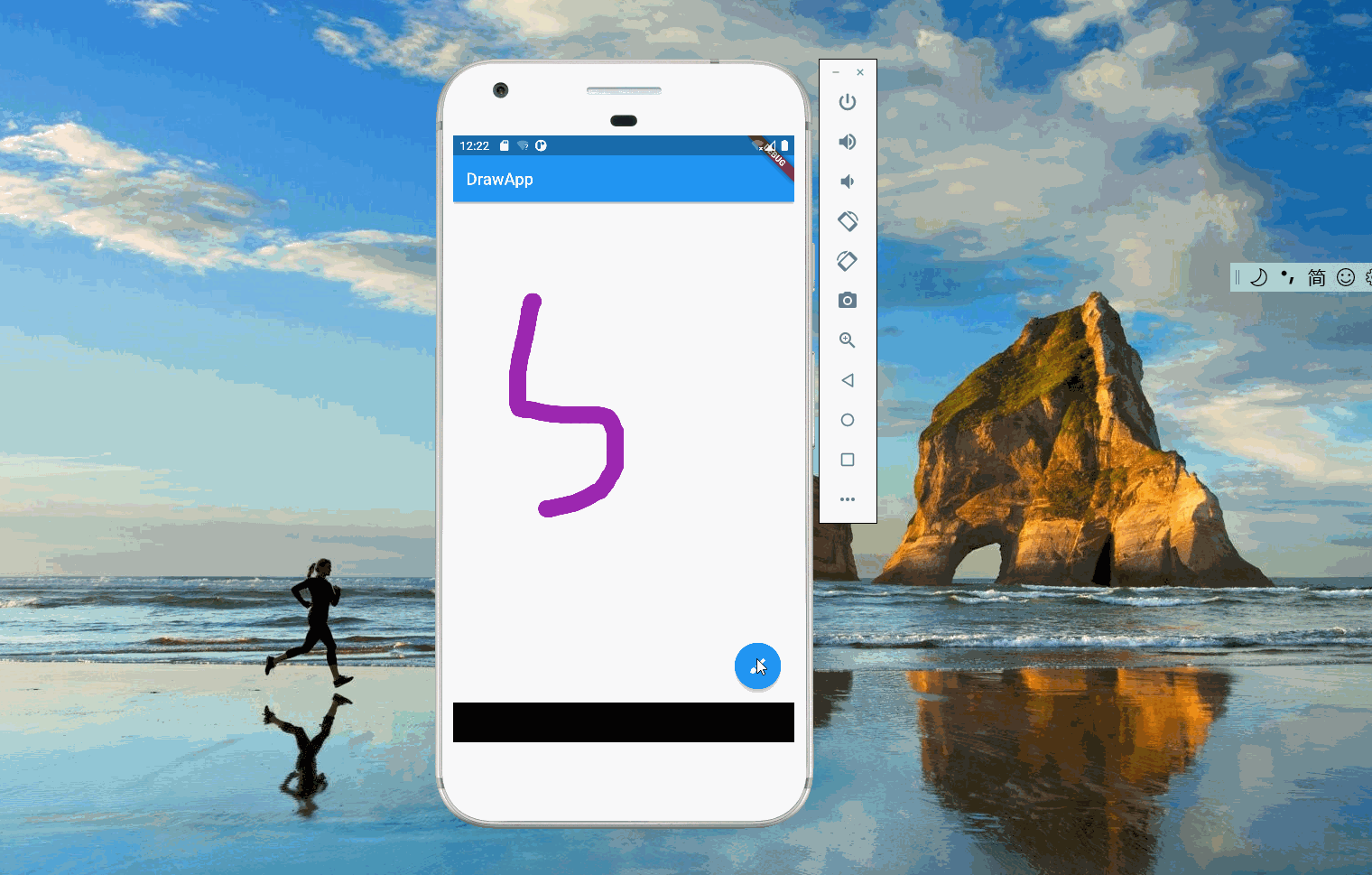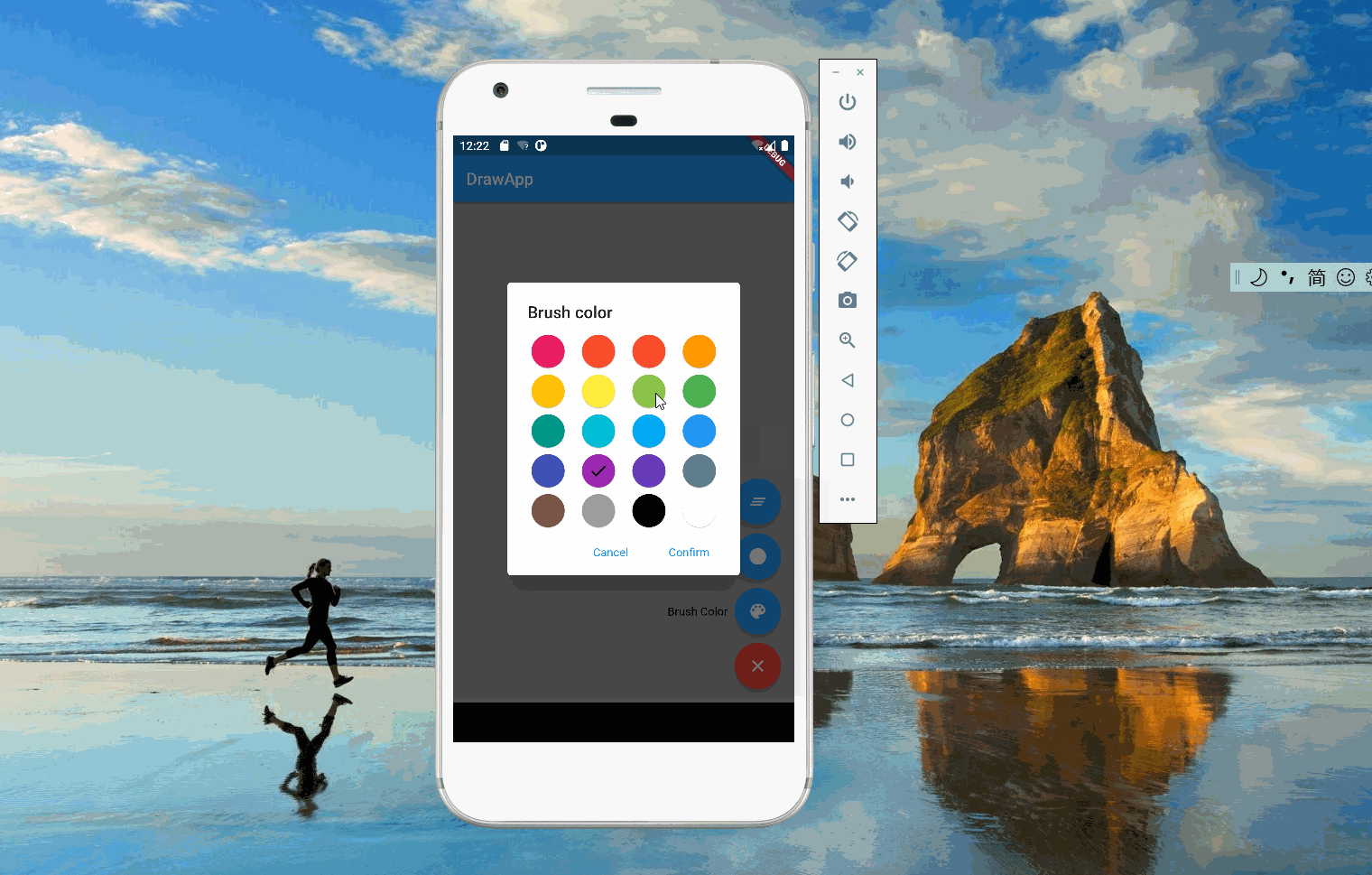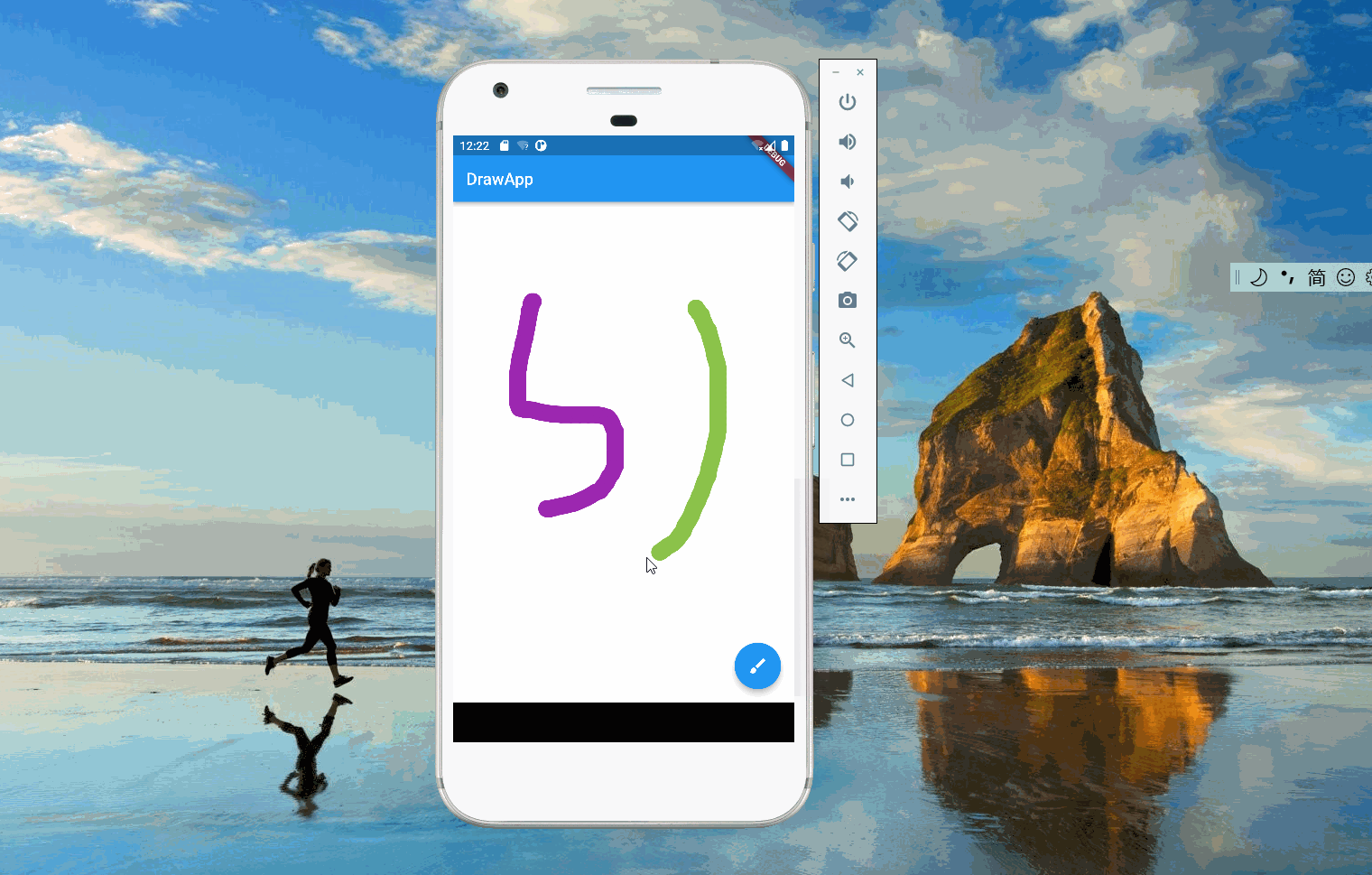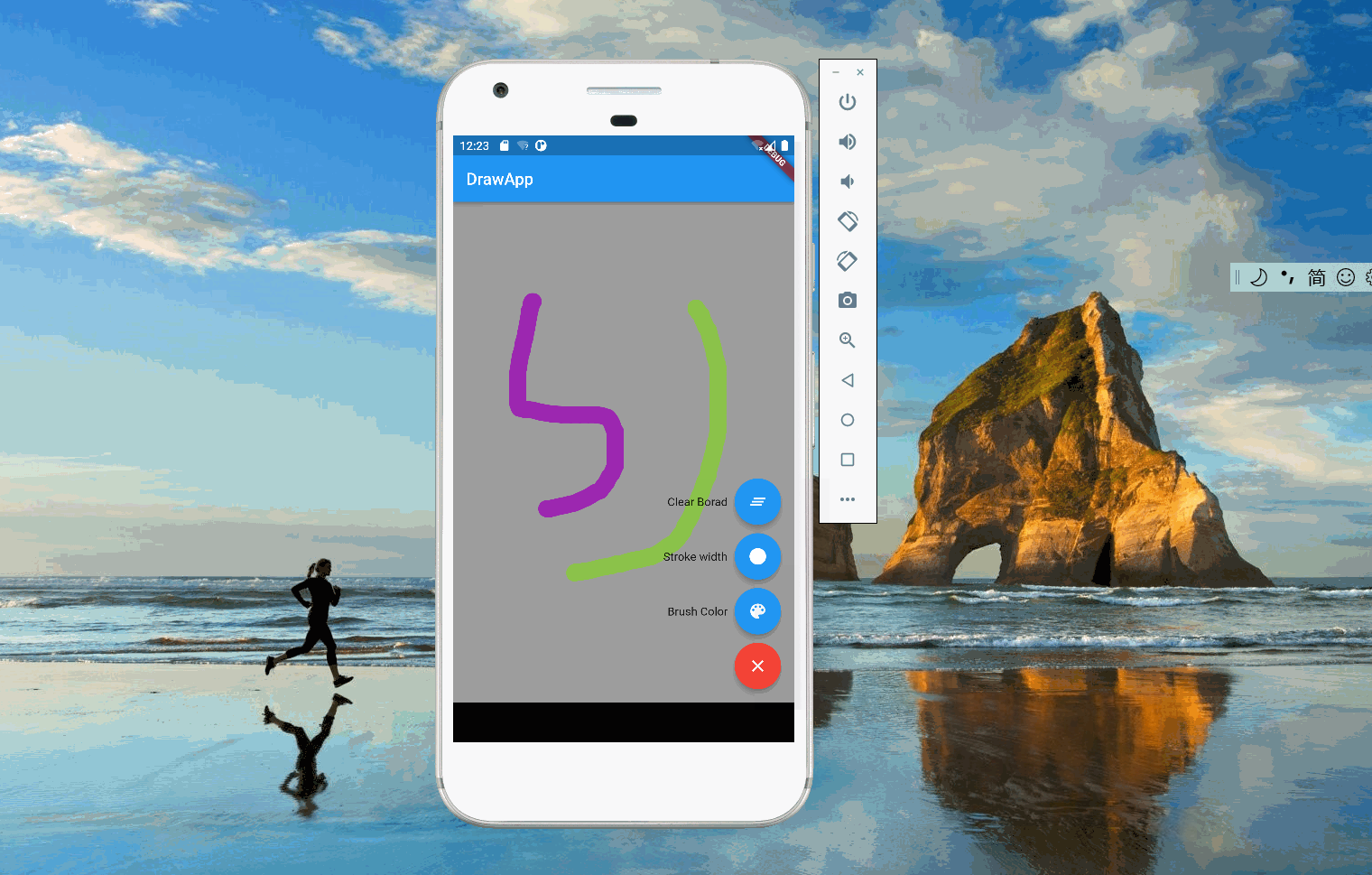
2. 线条定义
线条描述了一系列的点的集合,这些点的连线就构成了线条。因为系统允许用户修改线条的颜色和直径,所以线条里定义了color和strokeWidth。
class PaintStroke {
final Color color;
final double strokeWidth;
//线条里面包含很多点
final List<Offset> paintedPoint;
const PaintStroke(this.color, this.strokeWidth, this.paintedPoint);
}
3. bloc定义
和画板菜单一样,画板也采用 bloc 来管理状态。cubit 定义如下,onPanDown表示用户按下屏幕,这时会准备新的线条(Stroke)。onPanUpdate表示用户在移动,这时将点加入到当前正在画的线条中。
import 'dart:math';
import 'package:bloc/bloc.dart';
import 'package:draw_app_bloc/models/paint_stroker.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
part 'paint_stroke_state.dart';
class PaintStrokeCubit extends Cubit<PaintStrokeState> {
PaintStrokeCubit()
: super(const NormalPaintStrokeState([], Colors.pink, 10.0));
changeColor(Color c) =>
emit(UnPaintStrokeState(state.strokes, c, state.currentWidth));
changeWidth(double width) =>
emit(UnPaintStrokeState(state.strokes, state.currentColor, width));
//新的stroke
onPanDown(Offset offset) {
PaintStroke p =
PaintStroke(state.currentColor, state.currentWidth, [offset]);
emit(NormalPaintStrokeState(
[...state.strokes, p], state.currentColor, state.currentWidth));
}
//往最后一个stroke里添加点
onPanUpdate(Offset offset) {
state.strokes[state.strokes.length - 1].paintedPoint.add(offset);
emit(NormalPaintStrokeState(
state.strokes, state.currentColor, state.currentWidth));
}
//清除所有线条
clearBoard() =>
emit(NormalPaintStrokeState([], state.currentColor, state.currentWidth));
}
state 的定义如下,currentColor和currentWidth表示当前画笔的颜色和线条的直径,菜单修改会反应到这两个变量上。新线条生成时会取currentColor和currentWidth。
UnPaintStrokeState针对修改颜色和修改画笔直径,这两种事件不需要重新绘制画板,所以画板接受到 state 后,会过滤掉UnPaintStrokeState。
这里需要实现==,因为 bloc 在emit时,会判断前后两个 state 是否相等,如果相等就不会传递。
class PaintStrokeState {
const PaintStrokeState(this.strokes, this.currentColor, this.currentWidth);
//所有的线条
final List<PaintStroke> strokes;
//当前的颜色
final Color currentColor;
//当前线条的直径
final double currentWidth;
//bloc的emit方法会对比前后两个状态,除非全部深拷贝,否则前后两次会相等
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) => false;
}
//修改颜色或者线条的状态
class UnPaintStrokeState extends PaintStrokeState {
const UnPaintStrokeState(
super.stokes, super.currentColor, super.currentWidth);
}
class NormalPaintStrokeState extends PaintStrokeState {
const NormalPaintStrokeState(
super.stokes, super.currentColor, super.currentWidth);
}
4. 绘画器
接下来介绍如何将线条(Stroke)绘制在屏幕上。在 flutter 里,通过继承CustomPainter,可以实现用户自定义画图。StrokePainter定义了paintState,接受的是 bloc 的绘制状态。绘制时,遍历所有线条(Stroke),将线条里的所有点用线(Line)连接起来,注意最后一个点因为没有后续,单独绘制一个点即可。
class StrokePainter extends CustomPainter {
PaintStrokeState paintState;
StrokePainter(this.paintState);
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
final paint = Paint();
for (PaintStroke st in paintState.strokes) {
paint.color = st.color;
paint.strokeWidth = st.strokeWidth;
paint.strokeCap = StrokeCap.round;
for (int i = 0; i < st.paintedPoint.length - 1; i++) {
canvas.drawLine(st.paintedPoint[i], st.paintedPoint[i + 1], paint);
}
canvas.drawPoints(PointMode.points,
[st.paintedPoint[st.paintedPoint.length - 1]], paint);
}
}
@override
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) {
return true;
}
}
5. 监听用户行为
flutter 提供了GestureDetector来捕获用户的行为,画图场景关注两个事件onPanDown和onPanUpdate,对应 bloc 里的两个方法。
GestureDetector(
onPanDown: (details) {
context.read<ShowDrawingCubit>().closeOption();
context
.read<PaintStrokeCubit>()
.onPanDown(details.localPosition);
},
onPanUpdate: (details) => context
.read<PaintStrokeCubit>()
.onPanUpdate(details.localPosition),
child: const LocalPainter(Colors.white),
)